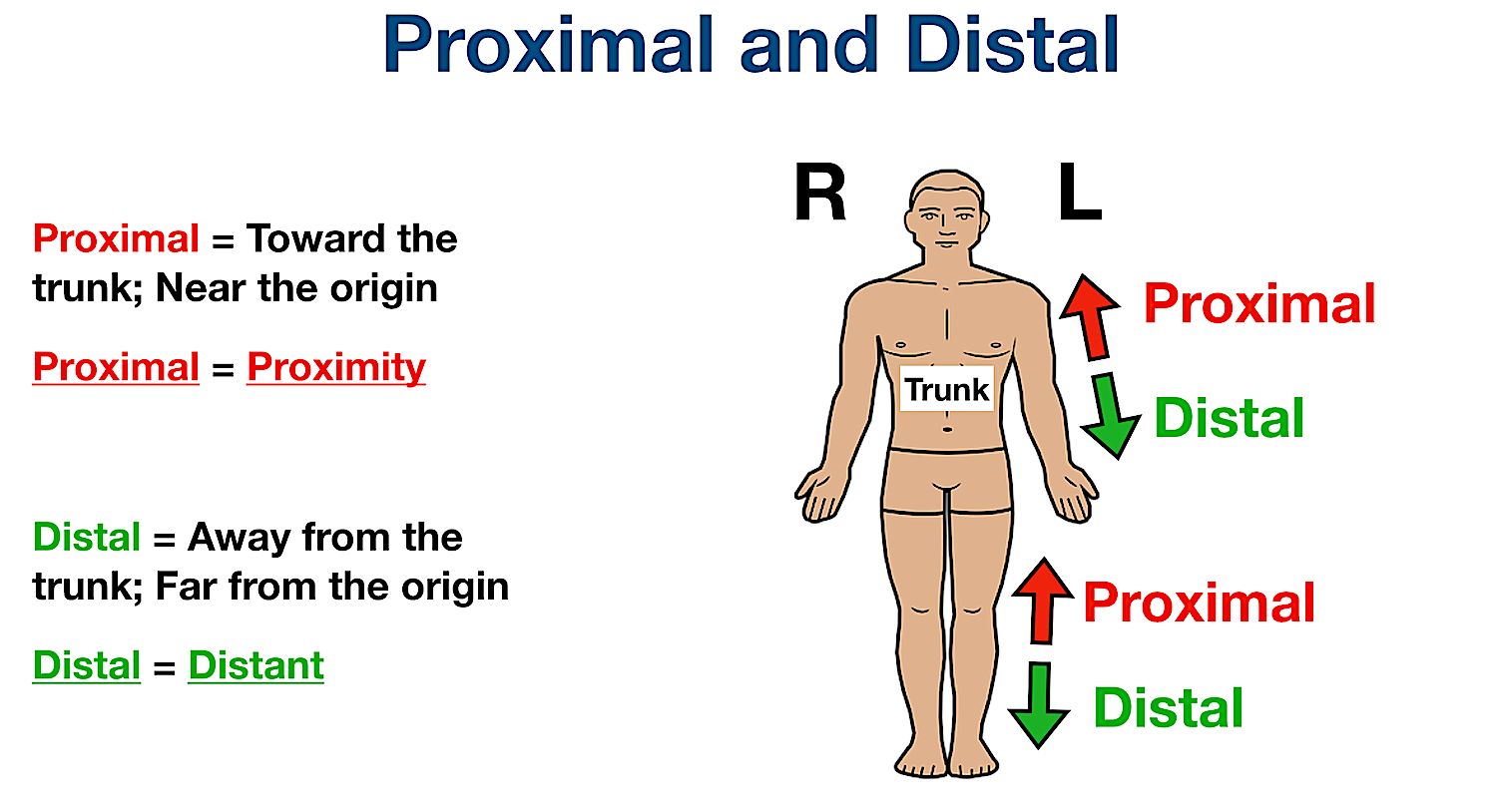
In the realm of human anatomy, a comprehensive comprehension of muscles is crucial for understanding how the body functions. Specifically, it is essential to differentiate between proximal and distal muscles as they play distinctive roles in our overall mobility and strength. Proximal muscles, located closer to the core, are responsible for providing stability and generating power, while distal muscles, situated further away from the core, control movements and fine motor skills. By unraveling the disparity between proximal and distal muscles, we gain a deeper understanding of the intricate workings of our bodies and how they contribute to our physical well-being.
Understanding the Difference: Proximal vs Distal Muscles
In the field of anatomy and physiology, understanding the difference between proximal and distal muscles is essential for comprehending the complex workings of the human body. The terms proximal and distal refer to the relative location of muscles in relation to a specific reference point. Proximal muscles are those that are closer to the body’s midline or center, while distal muscles are located further away from the midline.

Anatomy of Proximal and Distal Muscles
To gain a better understanding of proximal and distal muscles, it is important to explore their anatomical features. Proximal muscles typically originate from the core or trunk of the body, including the chest, abdomen, and pelvis. They have larger muscle bellies and stronger tendons, allowing for increased force production. Distal muscles, on the other hand, originate further away from the body’s midline, such as the limbs and extremities. These muscles often have longer tendons and are responsible for fine motor movements and intricate tasks.
Location and Function of Proximal Muscles
When it comes to understanding the location and function of proximal muscles, it is necessary to identify the major muscles within this category. The major proximal muscles include the pectoralis major, latissimus dorsi, deltoids, and the core muscles such as the rectus abdominis and obliques. Proximal muscles play a significant role in providing stability and support to the body, as well as generating power for various movements. They are involved in activities such as lifting, pushing, and pulling, and contribute to overall posture and balance.

Location and Function of Distal Muscles
In contrast to proximal muscles, distal muscles are mainly located in the limbs and extremities. Some major distal muscles include the biceps brachii, triceps brachii, quadriceps, and gastrocnemius. Distal muscles are responsible for precise movements, such as gripping, writing, and walking. Their key function is to enable fine motor skills and control the movement of the joints. These muscles work in coordination with proximal muscles to ensure smooth and controlled actions.
Muscle Strength and Proximal vs Distal Muscles
Understanding the benefits of strong proximal and distal muscles is crucial for individuals looking to optimize their physical performance and overall well-being. Strong proximal muscles provide a solid foundation for power generation, stability, and injury prevention. They contribute to improved balance, posture, and overall body mechanics. On the other hand, strong distal muscles enhance dexterity, coordination, and precision in movements. They allow individuals to carry out intricate tasks with ease, such as performing surgery or playing a musical instrument.

Training Techniques for Proximal Muscles
When it comes to training proximal muscles, a combination of resistance exercises, core stabilization exercises, and functional movements can be implemented. Resistance exercises such as squats, deadlifts, and bench presses target major proximal muscles while engaging stabilizing muscles. Core stabilization exercises, such as planks and Russian twists, help strengthen the deep muscles of the abdomen and lower back. Functional movements, such as lifting and carrying heavy objects, should be incorporated as well to simulate real-life activities and enhance overall strength.
Training Techniques for Distal Muscles
Training distal muscles requires a different approach due to their involvement in precise movements. Resistance exercises that isolate specific muscle groups, such as bicep curls and tricep extensions, can be incorporated. Additionally, incorporating exercises that challenge fine motor skills and coordination, such as hand-eye coordination drills or balance training, can help enhance distal muscle performance. It is important to gradually increase the intensity and difficulty of the exercises to ensure proper progression and prevent overuse injuries.

Common Injuries and Proximal vs Distal Muscles
Understanding the specific injuries that may occur in proximal and distal muscles is crucial for diagnosing and treating them effectively. Proximal muscle injuries commonly involve strains or tears in the larger muscle groups, resulting from activities involving excessive force or sudden movements. Distal muscle injuries, on the other hand, often involve overuse injuries, such as tendonitis or stress fractures, due to repetitive motions or improper form. Proper warm-up, adequate rest and recovery, and using proper form during exercise are vital in preventing both proximal and distal muscle injuries.
Rehabilitation and Proximal vs Distal Muscles
The rehabilitation process for proximal and distal muscle injuries may differ depending on the specific injury and its location. In the case of proximal muscle injuries, rehabilitation typically focuses on restoring strength, flexibility, and coordination. Physical therapy may involve exercises targeting the injured muscle group, as well as the surrounding muscles and joints to ensure proper alignment and balance. For distal muscle injuries, rehabilitation often involves more targeted exercises to rebuild strength and coordination in the affected area, often including proprioception and balance training.
Prevention and Maintenance of Proximal and Distal Muscles
Preventing injuries to both proximal and distal muscles is crucial for maintaining optimal physical health. To prevent proximal muscle injuries, it is essential to maintain overall body strength and flexibility through regular strength training and stretching exercises. Adequate warm-up before physical activities and utilizing proper form during exercise can also help prevent these injuries. When it comes to maintaining both proximal and distal muscles, consistency is key. Incorporating a well-rounded exercise routine that targets all major muscle groups, including the proximal and distal muscles, is crucial for maintaining overall muscle health and function.
In conclusion, understanding the difference between proximal and distal muscles is essential for anyone seeking to enhance their physical performance and overall well-being. Proximal muscles provide stability and power, while distal muscles contribute to precise movements and fine motor skills. By incorporating appropriate training techniques, preventing injuries, and engaging in proper rehabilitation, individuals can maintain strong and functional proximal and distal muscles, leading to improved physical performance and overall health.