In this article, we explore the topic of purulent drainage, examining its causes, symptoms, and treatment. Purulent drainage refers to the discharge of pus from an infected wound or abscess. It is a common sign of an underlying infection and can occur in various parts of the body. Understanding the causes and symptoms of purulent drainage is essential for proper diagnosis and timely intervention. With accurate and factual information, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of this topic for our readers on our health website.

Definition
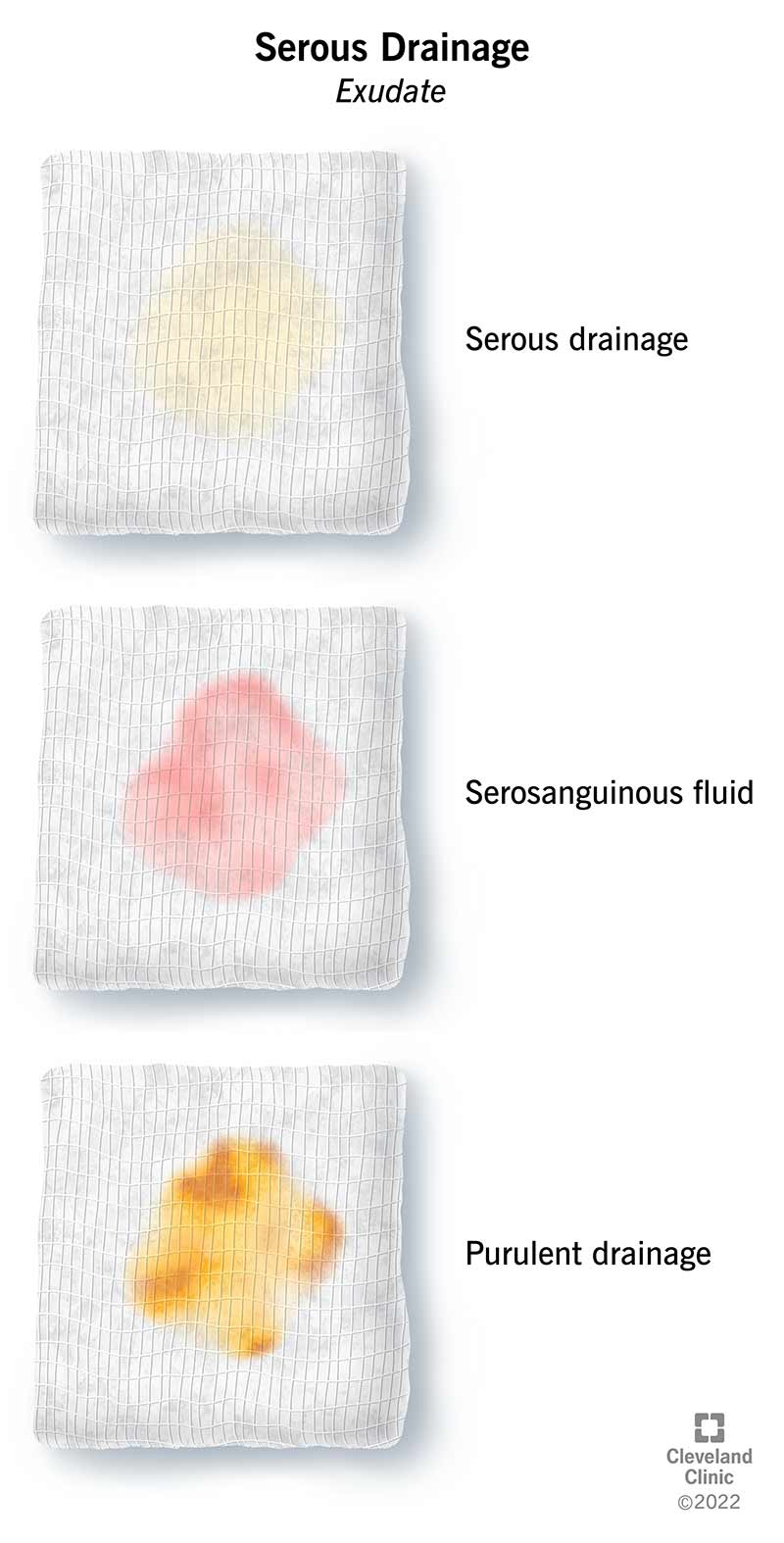
What is purulent drainage?
Purulent drainage refers to the presence of pus, a thick and yellowish or greenish fluid, in wounds or abscesses. Pus is a natural response of the immune system to fight infection, and it consists of white blood cells, dead tissue, and bacteria. Purulent drainage is typically a sign of an underlying infection or inflammation, and it often indicates a need for medical attention and prompt treatment.
Characteristics of purulent drainage
Purulent drainage can vary in color, consistency, and odor, depending on the specific infection or underlying condition. It is commonly described as yellow or green but can also appear brown or white. The fluid is often thick and sticky, resembling cottage cheese or creamy yogurt. Additionally, purulent drainage can emit a foul odor due to the presence of bacteria and necrotic tissue. These characteristics help healthcare professionals determine the nature and severity of the infection or wound.
Causes
Bacterial infection
One of the primary causes of purulent drainage is a bacterial infection. Bacteria can enter the body through open wounds, surgical incisions, or areas of compromised tissue. Common bacterial culprits include Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. When the immune system detects the presence of bacteria, it triggers an inflammatory response, resulting in the secretion of pus.
Abscess formation
An abscess is a localized collection of pus, usually surrounded by a wall of inflamed tissue. It can occur in various parts of the body, such as the skin, internal organs, or deep within the muscles. Abscesses often develop as a result of bacterial infection or as a response to foreign bodies, such as splinters or catheters. They can cause intense pain and swelling, and if left untreated, may burst and release purulent drainage.
Foreign body presence
Purulent drainage can also occur in response to foreign bodies lodged in the body. When a foreign object, such as a piece of glass or a splinter, enters the skin or soft tissues, it can trigger an immune response, leading to the formation of pus. The body attempts to isolate and eliminate the foreign material, which can result in the formation of an abscess or localized infection.
Surgical site infection
Following surgical procedures, there is a risk of developing an infection at the incision site. If bacteria enter the wound during surgery or post-operative care, it can lead to an infection and subsequent purulent drainage. Surgical site infections can cause severe complications if not promptly treated, such as delayed wound healing, increased pain, and the potential for systemic infection.
Chronic inflammatory conditions
Certain chronic inflammatory conditions, such as osteomyelitis (infection of the bone), septic arthritis (joint infection), or chronic sinusitis, can also lead to purulent drainage. These conditions often involve ongoing inflammation and the presence of bacteria. The immune response in these cases results in the production of pus as an attempt to combat the infection.

Symptoms
Presence of pus
The most prominent and defining symptom of purulent drainage is the presence of pus. Pus is typically thick and appears yellow or green. Its presence in wounds or areas of infection indicates an ongoing battle between the immune system and bacteria or foreign substances.
Redness and inflammation
In addition to the presence of pus, purulent drainage is often accompanied by redness and inflammation in the affected area. These signs indicate an immune response and increased blood flow to the site of infection or injury.
Pain or tenderness
Pain or tenderness at the site of purulent drainage is a common symptom. The inflammation and pressure caused by the accumulation of pus can lead to discomfort, sensitivity, or throbbing pain.
Foul odor
Purulent drainage often emits a foul odor due to the breakdown of necrotic tissue and the metabolic activities of bacteria. The smell can be unpleasant and strong, alerting individuals to the presence of an infection or abscess.
Fever or chills
Systemic symptoms, such as fever or chills, may accompany purulent drainage. These symptoms indicate that the infection has spread beyond the localized area and may be progressing into a more serious systemic infection.
Diagnosis
Physical examination
A healthcare professional will typically start the diagnostic process by conducting a thorough physical examination. They will assess the location, size, and characteristics of the purulent drainage, as well as evaluate the surrounding tissue for signs of infection or inflammation.
Analysis of drainage
To further determine the cause of purulent drainage, a sample of the fluid may be obtained and analyzed. The sample can provide valuable information about the type and extent of the infection, as well as aid in selecting appropriate treatment options.
Microbiological cultures
Microbiological cultures involve taking a sample of the purulent drainage and growing it in a laboratory setting to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection. This process helps healthcare providers select the most effective antibiotics for treatment.
Imaging studies
In some cases, imaging studies such as X-rays, ultrasounds, or computed tomography (CT) scans may be ordered to evaluate the extent of the infection, identify any abscesses, or detect the presence of foreign bodies.
Complications
Spread of infection
If not properly treated, purulent drainage and the associated infection can spread to surrounding tissues, leading to a more extensive infection. This can result in complications such as cellulitis, osteomyelitis, or sepsis, which can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Delayed wound healing
Purulent drainage can interfere with the normal healing process. The presence of bacteria and necrotic tissue can slow down or prevent wound closure, leading to delayed wound healing. This delay increases the risk of infection and may require more intensive wound care.
Abscess formation
Purulent drainage can be a precursor to abscess formation. The pocket of pus can enlarge, causing increased pain, swelling, and the potential for rupture. Abscesses often require drainage and sometimes surgical intervention to promote healing.
Systemic infection
Without proper treatment, the infection causing purulent drainage can spread throughout the body, leading to a systemic infection. This can result in severe symptoms such as high fever, rapid heart rate, low blood pressure, and organ dysfunction. Immediate medical attention is critical to prevent serious complications.
Treatment
Drainage and irrigation
Drainage and irrigation are often necessary to remove pus and debris from the affected area. This can be done through a variety of methods, including manual irrigation, incision and drainage, or the use of specialized wound dressings to promote healing.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to treat bacterial infections associated with purulent drainage. The specific antibiotic chosen will depend on the identified bacteria and its susceptibility to certain medications. It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed to ensure eradication of the infection.
Wound care
Proper wound care is essential for the management of purulent drainage. This may involve regular cleansing of the wound with sterile solutions, applying appropriate dressings, and promoting a clean and moist environment to facilitate healing.
Surgical intervention
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to drain abscesses or remove foreign bodies causing the infection. Surgery allows for a more thorough cleaning of the affected area and can help prevent further complications.
Management of underlying condition
For individuals with chronic inflammatory conditions contributing to purulent drainage, managing the underlying condition is crucial. This may involve medications to control inflammation, lifestyle modifications, and close monitoring by healthcare professionals.

Prevention
Proper wound care
Practicing proper wound care is essential to prevent the development of purulent drainage. This includes cleaning wounds promptly, applying appropriate dressings, and keeping the area clean and dry. Following surgical procedures, adhering to recommended post-operative wound care instructions is critical.
Hygiene practices
Maintaining good personal hygiene is crucial to prevent the introduction of bacteria into open wounds or compromised tissues. Regular handwashing, especially before and after wound care, can help reduce the risk of infection.
Personal protective equipment
When dealing with potentially infectious materials, healthcare providers should always wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves, masks, and gowns. This helps minimize the risk of contaminating wounds or spreading infections.
Preventive antibiotics
In certain situations, healthcare providers may prescribe preventive antibiotics to individuals at high risk of developing purulent drainage or infection after specific procedures or injuries. These antibiotics help reduce the risk of bacterial colonization and subsequent infection.
Home Care
Cleanse the wound
For individuals with purulent drainage at home, proper wound cleansing is crucial. This involves washing the affected area gently with mild soap and water or a sterile saline solution. It is important to avoid using harsh or irritating substances that may further damage the tissue.
Dress the wound
Applying appropriate dressings to the wound can help protect it from further contamination and facilitate healing. The choice of dressing will depend on the amount of drainage, the stage of wound healing, and healthcare provider recommendations.
Keep the area dry
Keeping the area around the drainage site dry is essential to prevent bacterial growth and infection. Regularly change dressings and avoid prolonged exposure to moisture, as this can impair the healing process.
Monitor for changes
Carefully monitor the wound and surrounding area for any changes or signs of worsening infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or fever. If any concerning symptoms arise, seek medical attention promptly.
Follow medical advice
It is critical to follow all medical advice provided by healthcare professionals. This includes taking prescribed medications as directed, attending follow-up appointments, and reporting any significant changes or concerns.

When to Seek Medical Attention
Worsening symptoms
If symptoms of purulent drainage, such as redness, swelling, or pain, worsen despite home care measures, medical attention should be sought. Worsening symptoms may indicate a progressing infection that requires further evaluation and treatment.
Signs of systemic infection
The development of systemic symptoms, such as high fever, rapid heart rate, confusion, or difficulty breathing, should never be ignored. These signs may indicate a spreading infection and require immediate medical attention.
Absence of improvement
If there is no improvement in symptoms or wound healing despite proper home care and adherence to medical advice, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for further assessment. This may indicate the need for a change in treatment or additional interventions.
Significant pain or discomfort
Severe or uncontrolled pain, or persistent discomfort in the affected area, warrants medical attention. Pain may indicate an abscess or the need for further examination to identify the underlying cause of purulent drainage.
Conclusion
Prompt and appropriate treatment of purulent drainage is vital to prevent complications and promote complete recovery. Early identification of the underlying cause, thorough diagnostic evaluation, and targeted treatment options tailored to each individual case are essential steps in managing this condition. By adhering to proper wound care, practicing good personal hygiene, and seeking medical attention when necessary, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of developing purulent drainage and associated complications. Continuous monitoring and timely follow-up are crucial aspects of successful management, ensuring the best possible outcomes for those affected.