Elevated liver enzymes, a common medical concern, can be indicative of various health conditions. In our article, “Understanding Elevated Liver Enzymes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment,” we aim to provide accurate and factual information to help readers grasp the underlying causes, identify potential symptoms, and explore possible treatment options. By delving into this topic, we hope to equip individuals with the necessary understanding to take proactive steps towards liver health and seek appropriate medical attention if necessary.
Understanding Elevated Liver Enzymes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment

Definition and Introduction to Liver Enzymes
Liver enzymes are proteins produced by the liver that play a crucial role in various biochemical reactions in the body. The liver produces several enzymes, including alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT). Elevated liver enzymes, also known as hepatic enzyme elevation, refer to abnormal levels of these enzymes in the blood.
Different Types of Liver Enzymes
The liver enzymes mentioned earlier serve different functions. ALT and AST are mainly involved in liver cell metabolism, while ALP is crucial for bone and liver health. GGT, on the other hand, is involved in the transportation and metabolism of amino acids. Monitoring the levels of these enzymes can help healthcare providers identify potential liver disorders.
Normal Range of Liver Enzymes
The normal range of liver enzymes may vary slightly depending on the laboratory, but typically, ALT levels range from 7 to 55 units per liter (U/L) for men and 7 to 45 U/L for women. AST levels are usually between 8 and 48 U/L for men and 7 and 35 U/L for women. ALP levels differ with age and gender, ranging from 45 to 115 U/L in adults. GGT levels commonly range from 9 to 48 U/L for men and 7 to 32 U/L for women.
Causes of Elevated Liver Enzymes
Elevated liver enzymes can be caused by various factors, including liver diseases, medication use, alcohol consumption, and certain medical conditions. Understanding the underlying cause is crucial in determining the appropriate treatment and preventing further liver damage. Some common causes of elevated liver enzymes include:
Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
Excessive alcohol consumption is one of the leading causes of elevated liver enzymes. Heavy and chronic alcohol use can lead to conditions such as alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis, which can significantly affect liver function and enzyme levels. It is important to seek professional help to reduce or eliminate alcohol consumption to prevent further liver damage.

Hepatitis
Hepatitis, both viral and non-viral, can cause liver inflammation and lead to elevated liver enzyme levels. Viral hepatitis, such as hepatitis A, B, and C, can be transmitted through contaminated food, water, or blood. Non-viral hepatitis, such as autoimmune hepatitis, occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the liver.
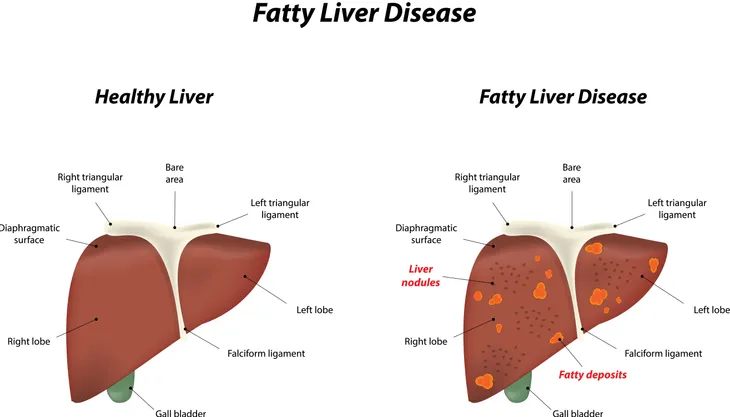
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver. It can be caused by obesity, high cholesterol, diabetes, or insulin resistance. NAFLD can lead to inflammation and liver enzyme elevation if left untreated.
Medications and Drugs
Certain medications and drugs can cause liver damage and result in elevated liver enzymes. Examples include acetaminophen (Tylenol), statins, antibiotics, antifungal medications, and some herbal supplements. It is essential to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications and supplements you are taking to monitor potential liver enzyme elevation.
Autoimmune Hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic condition in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the liver, leading to inflammation and elevated liver enzymes. This condition requires lifelong management and treatment to prevent liver damage and further complications.
Genetic Disorders
Some genetic disorders, such as Wilson disease and hemochromatosis, can cause elevated liver enzymes. These conditions disrupt the liver’s normal functioning and metabolism, leading to a buildup of certain substances that can damage liver cells and increase enzyme levels.

Other Possible Causes
In addition to the mentioned causes, there are several other factors that can lead to elevated liver enzymes. These include obesity, diabetes, certain infections, exposure to toxins or chemicals, gallbladder diseases, and liver tumors. Identifying the specific cause is essential for appropriate treatment.
Symptoms of Elevated Liver Enzymes
Elevated liver enzymes do not typically cause noticeable symptoms on their own. However, underlying conditions contributing to enzyme elevation may present symptoms. The severity of symptoms may vary depending on the cause and the extent of liver damage. Some common symptoms include:
Mild Symptoms
Mild symptoms of elevated liver enzymes may include fatigue, weakness, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, and unexplained weight loss. These symptoms may be non-specific and can often be attributed to other underlying health issues.
Severe Symptoms
When liver damage becomes severe, more noticeable symptoms may occur. These can include jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), dark urine, pale stools, easy bruising or bleeding, fluid retention, confusion, and changes in mental function. Seek medical attention immediately if experiencing any of these severe symptoms.
Signs of Chronic Liver Disease
Long-term liver enzyme elevation can lead to chronic liver disease. In addition to the symptoms mentioned earlier, chronic liver disease may also cause spider veins, enlarged spleen, swelling in the legs and abdomen, and a tendency to bleed easily. Regular monitoring and medical intervention are crucial in managing chronic liver disease.

Complications of Long-Term Liver Enzyme Elevation
If left untreated, long-term elevation of liver enzymes can lead to severe complications. These include liver cirrhosis, liver failure, increased risk of liver cancer, and portal hypertension. Early detection and appropriate treatment are vital in preventing the progression of these complications.
Diagnosing Elevated Liver Enzymes
Diagnosing the cause of elevated liver enzymes involves a comprehensive evaluation of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. The diagnostic process may include:
Medical History and Physical Examination
Your healthcare provider will review your medical history, inquire about symptoms, medication use, alcohol consumption, and potential risk factors. A physical examination may reveal signs of liver damage, such as an enlarged liver or tenderness in the abdomen.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are essential for assessing liver function and enzyme levels. Common tests include liver function tests (LFTs), which measure ALT, AST, ALP, GGT, and bilirubin levels. Additional tests, such as viral hepatitis markers and autoimmune antibodies, may also be conducted to determine the underlying cause.
Additional Diagnostic Imaging
In some cases, additional diagnostic imaging may be required to assess the liver’s structure and identify any abnormalities. This may involve ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scan, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or liver elastography.
Liver Biopsy
A liver biopsy may be recommended in certain cases to obtain a small sample of liver tissue for further analysis. This procedure can provide valuable information about the extent of liver damage and assist in determining the most appropriate treatment plan.
Treating Elevated Liver Enzymes
The treatment of elevated liver enzymes focuses on addressing the underlying cause, promoting liver health, and preventing further damage. The treatment approach may involve a combination of the following:
Underlying Cause Treatment
Treating the underlying cause of elevated liver enzymes is essential for long-term management. Depending on the cause, treatment may involve medication for viral hepatitis, lifestyle modifications, management of autoimmune disorders, or interventions to address metabolic and genetic conditions.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial in maintaining liver health. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy body weight. Obesity and excessive alcohol use can exacerbate liver damage and enzyme elevation.
Medications and Therapies
In some cases, medications or therapies may be prescribed to manage specific liver conditions. These may include antiviral medications for hepatitis, immunosuppressants for autoimmune hepatitis, and medications to control diabetes or high cholesterol levels. It is important to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions and regularly monitor liver function.
Nutritional Support
Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in promoting liver health. Nutritional support may involve dietary adjustments to reduce fat intake, increase consumption of antioxidants and nutrients beneficial for liver function, and supplementation as recommended by a healthcare provider or registered dietitian.
Liver Transplantation
In severe cases of chronic liver disease or liver failure, a liver transplantation may be necessary. This involves surgically replacing the diseased liver with a healthy liver from a donor. Liver transplantation is a complex procedure and is considered when all other treatment options have been exhausted.
Prevention and Management of Elevated Liver Enzymes
Prevention and management strategies are essential in maintaining optimal liver health and preventing further elevation of liver enzymes. These include:
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
Leading a healthy lifestyle is paramount in preventing liver damage. This includes consuming a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy body weight, and avoiding risky behaviors such as excessive alcohol consumption and illicit drug use.
Safe Medication Usage
Be cautious when using medications and herbal supplements. Always follow the recommended dosage and consult healthcare professionals before starting new medications, especially if you have a history of liver disease or have elevated liver enzymes.
Regular Health Check-ups
Regular health check-ups are important for early detection of any underlying liver conditions. Stay up-to-date with routine blood tests and liver function tests as recommended by your healthcare provider.
Avoiding Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Limit alcohol consumption to reduce the risk of liver damage. If you have a history of alcohol-related liver disease or elevated liver enzymes, it is essential to seek professional help to quit or reduce alcohol intake.
Vaccination against Hepatitis
Vaccination against hepatitis A and B is highly recommended to prevent these viral infections. Hepatitis A can be prevented through good hygiene practices, such as handwashing, and hepatitis B vaccination is a key preventive measure.
Monitoring and Managing Chronic Liver Diseases
If you have been diagnosed with a chronic liver disease, regular monitoring and appropriate management are vital. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions, take prescribed medications as directed, and attend regular check-ups to prevent disease progression and further liver damage.
Conclusion
Understanding elevated liver enzymes is crucial in identifying the underlying causes, recognizing symptoms, and implementing appropriate treatment strategies. Early detection and intervention can help prevent further liver damage and reduce the risk of complications. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, following recommended medical guidance, and seeking timely medical attention, individuals can maintain optimal liver health and overall well-being.